Forever Scalable
Neuraldig is a Python based toolkit for writing Command-Line Interface(CLI) applications. Quo is making headway towards composing speedy and orderly CLI applications while forestalling any disappointments brought about by the failure to execute a CLI API. Simple to code, easy to learn, and does not come with needless baggage.
Neuraldig works flawlessly with Linux, OSX, and Windows.
Neuraldig requires Python 3.8 or later.
- Support for Ansi, RGB and Hex color models
- Support for tabular presentation of data
- Intuitive progressbars
- Code completions
- Nesting of commands
- Customizable Text User Interface (TUI) dialogs.
- Automatic help page generation
- Syntax highlighting
- Autosuggestions
- Key Binders
You can install quo via the Python Package Index (PyPI)
pip install -U quo
Run the following to test Quo output on your terminal:
python -m quo
To output formatted text to your terminal you can import the echo method. Try this:
Example 1
from quo import echo
echo(f"Hello, World!", fg="red", italic=True, bold=True))Example 2
from quo import echo
echo(f"Quo is ", nl=False)
echo(f"scalable", bg="red", fg="black") Alternatively, you can import print
from quo import print
from quo.text import Text
print(Text('<b>This is bold</b>'))
print(Text('<i>This is italic</i>'))
print(Text('<u>This is underlined</u>'))
# Colors from the ANSI palette.
print(Text('<red>This is red</red>'))
print(Text('<style fg="green" bg="red">Green on red background</stlye>'))- Using
quo.promptmethod.
from quo import prompt
prompt("What is your name?")- Using
quo.prompt.Promptobject
from quo.prompt import Prompt
session = Prompt()
session.prompt("Type something:") Read more on Prompt
Quo contains a number of builtin features you can use to create elegant output in your CLI.
Click the following headings for details:»
Console
For more control over quo terminal content, import and construct a `Console` object.
from quo import Console
console = Console()Quo supports launching applications through Console.launch. This can be used to open the default application associated with a URL or filetype.
from quo import Console
console = Console()
console.launch("https://quo.rtfd.io/")
Read more on Console
Completion
Press [Tab] to autocomplete
from quo.prompt import Prompt
from quo.completion import WordCompleter
example = WordCompleter(['USA', 'UK', 'Canada', 'Kenya'])
session = Prompt(completer=example)
session.prompt('Which country are you from?: ')Auto suggestion is a way to propose some input completions to the user. Usually, the input is compared to the history and when there is another entry starting with the given text, the completion will be shown as gray text behind the current input. Pressing the right arrow → or ctrl-e will insert this suggestion, alt-f willinsert the first word of the suggestion.
from quo.prompt import Prompt
from quo.completion import AutoSuggestFromHistory
from quo.history import InMemoryHistory
history = InMemoryHistory(
history.append("import os")
history.append('print("hello")')
history.append('print("world")')
history.append("import path"
session = Prompt(auto_suggest=AutoSuggestFromHistory(), history=history)
while True:
session.prompt('> ')Read more on Completions
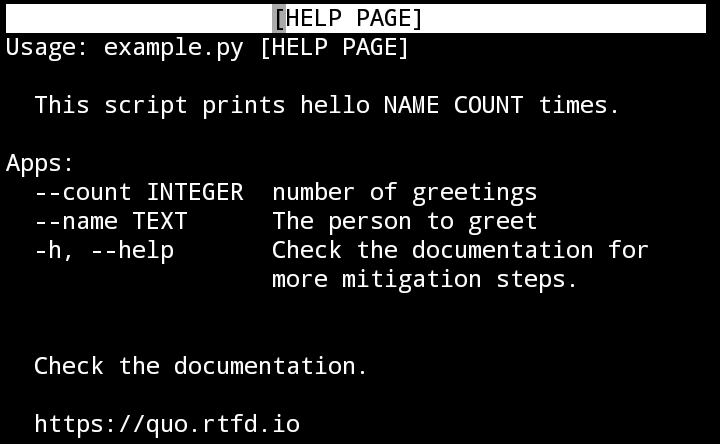
Documenting Scripts
Quo automatically generates help pages for your command-line tools. from quo import print
from quo.console import command
from quo.console import app
@command()
@app('--count', default=1, help='number of greetings')
@app('--name', prompt="What is your name?", help="The person to greet")
def hello(count: int, name: str):
"""This script prints hello NAME COUNT times."""
for x in range(count):
print(f"Hello {name}!")
if __name__ == "__main__:
hello()Progress
Creating a new progress bar can be done by calling the class **ProgressBar** The progress can be displayed for any iterable. This works by wrapping the iterable (like ``range``) with the class **ProgressBar** import time
from quo.progress import ProgressBar
with ProgressBar() as pb:
for i in pb(range(800)):
time.sleep(.01)Read more on Progress
Key Binding
A key binding is an association between a physical key on a keyboard and a parameter.
from quo import echo
from quo.prompt import Prompt
from quo.keys import Bind
bind = Bind()
# Print "Hello world" when ctrl-h is pressed
@bind.add("ctrl-h")
def _(event):
echo("Hello, World!")
session.prompt(">>", bind=bind)Read more on Key bindings
Dialog
High level API for displaying dialog boxes to the user for informational purposes, or get input fromthe user.- Example of a message box dialog.
from quo.dialog import MessageBox
MessageBox(
title="Message pop up window",
text="Do you want to continue?\nPress ENTER to quit.").run() The above produces the following output

- Example of a prompt box dialog
from quo.dialog import PromptBox
PromptBox(
title="PromptBox shenanigans",
text="What Country are you from?:").run()Read more on Dialogs
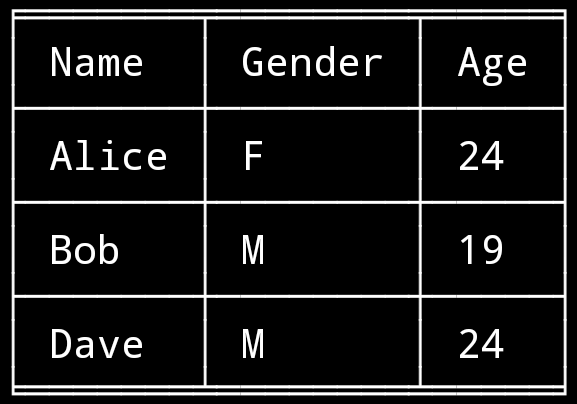
Table
Function Table offers a number of configuration options to set the look and feel of the table, including how borders are rendered and the style and alignment of the columns.
Example
from quo import echo
from quo.table import Table
data = [
["Name", "Gender", "Age"],
["Alice", "F", 24],
["Bob", "M", 19],
["Dave", "M", 24]
]
echo(Table(data))Widgets
A collection of reusable components for building full screen applications.Widget that displays the given text. It is not editable or focusable.
from quo.console import Console
from quo.keys import Bind
from quo.layout import Layout
from quo.widget import Label
root = Label("Hello, World", style="fg:black bg:red")
layout = Layout(root)
# Ctrl-c to exit
bind = Bind()
@bind.add("ctrl-c")
def _(event):
event.app.exit()
Console(
layout=layout,
bind=bind,
full_screen=True).run()Read more on Widgets
For more intricate examples, have a look in the examples directory and the documentation.
In order to for us to maintain this project and grow our community of contributors. Donate
Simple If you know Python you can easily use quo and it can integrate with just about anything.
For discussions about the usage, development, and the future of quo, please join our Google community
If you have any suggestions, bug reports, or annoyances please report them to our issue tracker at Bug tracker or send an email to:
This software is licensed under the MIT License. See the License file in the top distribution directory for the full license text.
Code of Conduct is adapted from the Contributor Covenant, version 1.2.0 available at Code of Conduct